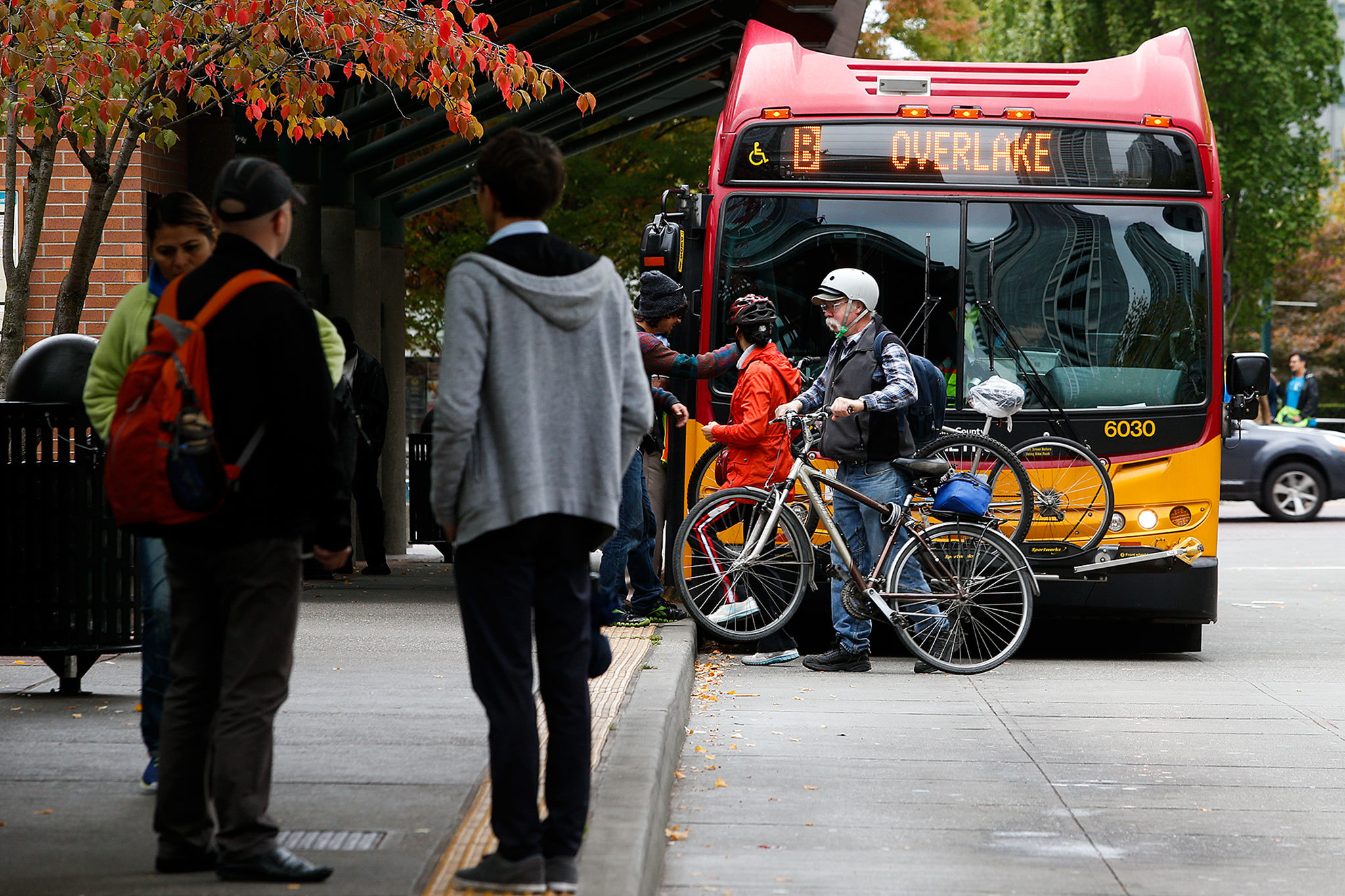In Seattle Weekly’s “Best of Seattle” reader poll this year, readers voted the D Line, which runs from downtown to Crown Heights, Seattle’s best bus route.
D Line driver Steve Ford wasn’t surprised. With far fewer stops than a conventional bus route and a ticketing system that allows people to board in the front or the back, he says riders appreciate the quicker rides through town. “You see how long it can take to get people on and off the bus. This eliminates a lot of that.”
The D Line is part of King County Metro’s RapidRide system, which is a form of what’s known as Bus Rapid Transit, or BRT, and the rider experience on the D Line could be a harbinger of things to come.
While building out the region’s light rail network is clearly the centerpiece of ST3, two vital corridors in the region would receive “Bus Rapid Transit” service under the plan, and the RapidRide system will get an infusion of funds to improve existing lines.
King County’s RapidRide system is considered “BRT-lite,” since it doesn’t feature many of the amenities more robust systems do. The buses have no dedicated lanes, meaning they are still subject to traffic congestion. Still, the lines, which began to roll out in 2010, do have traffic-signal priority — that is, lights turn green to get them through intersections — and a few special lanes they can use to bypass traffic. While some commuters continue to grumble that the rides are hardly rapid, the Weekly’s reader poll isn’t the only vote of confidence the buses have received. The three busiest RapidRide lines have about 50 percent more ridership than the lines they replaced.
Proponents of BRT argue that ST3 spends way too much on rail where it could just deploy buses. Done right, they say, most of the benefits of rail transit can be achieved for a fraction of the cost and with far more flexibility, since buses can be deployed elsewhere if ridership demand shifts. “Gold standard” BRT — a rarity in the United States but common in South America — features grade-separated lanes for buses as long as Link Light Rail trains.
Though still not up to Gold Standard, the new BRT lines planned for in ST3 are more robust than RapidRide, and the overall plan shows some of the advantages of BRT over light rail.
First, there’s the speed of building out the systems. The BRT lines in the plan will run along I-405/SR 518 and SR 522 — all Eastside highways that are notorious for their choked traffic and in need of quick relief. While many places promised light rail in ST3 will be waiting decades for the service to actually get built, the BRT lines are scheduled to be deployed by 2024.
Also, the cost-per-rider on the BRT lines is expected to be lower than with other Eastside projects. The I-405 BRT, running from Lynnwood to Burien, is estimated to cost between $687 million and $735 million to build (in 2014 dollars), and is expected to carry 11,000 to 13,000 riders per day by 2040. By comparison, the light rail between downtown Redmond and the Microsoft campus — a distance of 3.7 miles — is expected to cost between $1 billion and $1.1 billion and carry between 7,000 and 9,000 people.
However, those savings may come at the expense of reliability. Sound Transit would not be building a dedicated lane for buses along I-405 (though it would build a dedicated lane on SR 518 between Tukwila and Burien). In general, the buses will use general-purpose lanes, including the new Express Toll Lanes on I-405, which use a sliding rate to manage traffic volume. That may strike some as worrisome, since the Express Toll Lanes are already filling up and traffic is expected to get worse in coming years. While the Washington Department of Transportation says the express toll has achieved its goal of keeping traffic moving at 45 mph or faster 90 percent of the time, the toll is already routinely maxing out at $10, leading to questions of how long it will be until even $10 draws more drivers than the lane can handle.
A few cities along I-405 were also miffed that ST3 moved away from features entertained early in the planning process. This includes so-called “in-line stops” throughout the line that would allow riders to pick up the bus directly from the side of the freeway, rather than forcing the bus to get off and back onto the highway. The current plan includes two in-line stations — one in Kirkland and another in Renton — but Eastsiders wanted more, since in-line stops allow the line to serve more people with very little impact on travel time (a letter signed by the mayors of Bellevue, Bothell and several other cities questioned if the line even deserved to be called “BRT” at all, given what they perceived as a lack of investment in the line).
As far as what the actual service will look like, the I-405 BRT would run every 10 minutes during rush hours, and every 15 minutes for the rest of the day. There would be just 11 stops on the line, and it would take 87 minutes to get from Lynnwood to Burien. On the SR 522 end, there would be nine stops between UW Bothell and NE 145th in Seattle. Service frequency would be the same as I-405.
Last but not least: parking. The BRT projects would include construction of five new garages, creating 2,200 new parking spaces across the two lines.
dperson@seattleweekly.com